A PriorityQueue is used when the objects are supposed to be processed based on the priority. It is known that a queue follows First-In-First-Out algorithm, but sometimes the elements of the queue are needed to be processed according to the priority, that’s when the PriorityQueue comes into play.
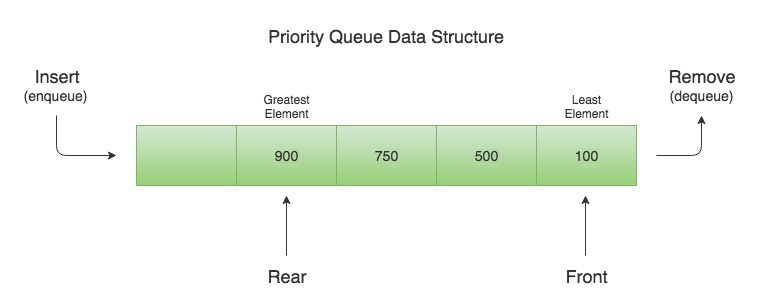
The PriorityQueue is based on the priority heap. The elements of the priority queue are ordered according to the natural ordering, or by a Comparator provided at queue construction time, depending on which constructor is used.
The head of the priority queue is the least element based on the natural ordering or comparator based ordering, if there are multiple objects with same ordering, then it can poll any one of them randomly. When we poll the queue, it returns the head object from the queue. For more additional info Java Online Course
Java Priority Queue size is unbounded but we can specify the initial capacity at the time of its creation. When we add elements to the priority queue, its capacity grows automatically.
PriorityQueue is not thread safe, so java provides PriorityBlockingQueue class that implements the BlockingQueue interface to use in java multithreading environment.
Java Priority Queue implementation provides O(log(n)) time for enqueing and dequeing method.
Java PriorityQueue Methods:
PriorityQueue class has below given important methods, you should know.
- boolean add(object) : Inserts the specified element into this priority queue.
- boolean offer(object) : Inserts the specified element into this priority queue.
- boolean remove(object) : Removes a single instance of the specified element from this queue, if it is present.
- Object poll() : Retrieves and removes the head of this queue, or returns null if this queue is empty.
- Object element() : Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue, or throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty.
- Object peek() : Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue, or returns null if this queue is empty.
- void clear() : Removes all of the elements from this priority queue.
- Comparator comparator() : Returns the comparator used to order the elements in this queue, or null if this queue is sorted according to the natural ordering of its elements. Learn more practical skills from Java Online Training
- boolean contains(Object o) : Returns true if this queue contains the specified element.
- Iterator iterator() : Returns an iterator over the elements in this queue.
- int size() : Returns the number of elements in this queue.
- Object[] toArray() : Returns an array containing all of the elements in this queue.
There are seven types of overloaded constructors by which we can set the argument to specify the initial capacity of the queue, supply Comparator to specify custom ordering of elements, or accept everything as default with a no-argument constructor.
- PriorityQueue()
- PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity)
- PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity, Comparator<? Super E> comparator)
- PriorityQueue(Commection<? extends E> c)
- PriorityQueue(Comparator<? Super E> comparator)
- PriorityQueue(PriorityQueue<? extends E> c)
- PriorityQueue(SortedSet<? extends E> c)
Take your career to new heights of success with a Java Certification Course
Example of Priority Queue:
package priorityqueue;
import java.util.Scanner;
class Task
{
String job;
int priority;
public Task(String job, int priority)
{
this.job = job;
this.priority = priority;
}
public String toString()
{
return "Job Name : "+ job +"\nPriority : "+ priority;
}
}
class PriorityQueue
{
private Task[] heap;
private int heapSize, capacity;
public PriorityQueue(int capacity)
{
this.capacity = capacity + 1;
heap = new Task[this.capacity];
heapSize = 0;
}
public void clear()
{
heap = new Task[capacity];
heapSize = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return heapSize == 0;
}
public boolean isFull()
{
return heapSize == capacity - 1;
}
public int size()
{
return heapSize;
}
public void insert(String job, int priority)
{
Task newJob = new Task(job, priority);
heap[++heapSize] = newJob;
int pos = heapSize;
while (pos != 1 && newJob.priority > heap[pos/2].priority)
{
heap[pos] = heap[pos/2];
pos /=2;
}
heap[pos] = newJob;
}
public Task remove()
{
int parent, child;
Task item, temp;
if (isEmpty() )
{
System.out.println("Heap is empty");
return null;
}
item = heap[1];
temp = heap[heapSize--];
parent = 1;
child = 2;
while (child <= heapSize)
{
if (child < heapSize && heap[child].priority < heap[child + 1].priority)
child++;
if (temp.priority >= heap[child].priority)
break;
heap[parent] = heap[child];
parent = child;
child *= 2;
}
heap[parent] = temp;
return item;
}
}
public class Priorityqueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Priority Queue Test\n");
System.out.println("Enter size of priority queue ");
PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue(scan.nextInt() );
char ch;
do
{
System.out.println("\nPriority Queue Operations\n");
System.out.println("1. insert");
System.out.println("2. remove");
System.out.println("3. check empty");
System.out.println("4. check full");
System.out.println("5. clear");
System.out.println("6. size");
int choice = scan.nextInt();
switch (choice)
{
case 1 :
System.out.println("Enter job name and priority");
pq.insert(scan.next(), scan.nextInt() );
break;
case 2 :
System.out.println("\nJob removed \n\n"+ pq.remove());
break;
case 3 :
System.out.println("\nEmpty Status : "+ pq.isEmpty() );
break;
case 4 :
System.out.println("\nFull Status : "+ pq.isFull() );
break;
case 5 :
System.out.println("\nPriority Queue Cleared");
pq.clear();
break;
case 6 :
System.out.println("\nSize = "+ pq.size() );
break;
default :
System.out.println("Wrong Entry \n ");
break;
}
System.out.println("\nDo you want to continue (Type y or n) \n");
ch = scan.next().charAt(0);
} while (ch == 'Y'|| ch == 'y');
}
}