Inheritance in Java is a mechanism in which one object acquires all the properties and behaviors of a parent object. It is an important part of OOPs (Object Oriented programming system).
The idea behind inheritance in Java is that you can create new classes that are built upon existing classes. When you inherit from an existing class, you can reuse methods and fields of the parent class. Moreover, you can add new methods and fields in your current class also.
Inheritance represents the IS-A relationship which is also known as a parent-child relationship. For more additional info Java Online Course
Important terminology:
- Super Class: The class whose features are inherited is known as superclass(or a base class or a parent class).
- Sub Class: The class that inherits the other class is known as subclass(or a derived class, extended class, or child class). The subclass can add its own fields and methods in addition to the superclass fields and methods.
- Reusability: Inheritance supports the concept of “reusability”, i.e. when we want to create a new class and there is already a class that includes some of the code that we want, we can derive our new class from the existing class. By doing this, we are reusing the fields and methods of the existing class.
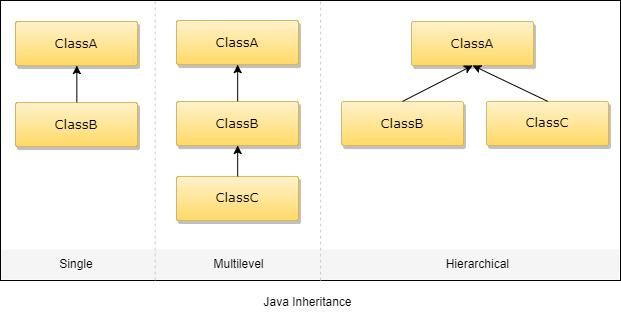
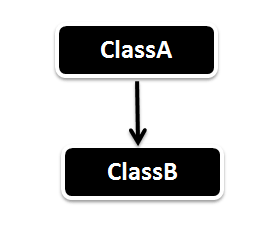
Single Inheritance in Java
Single Inheritance is the simple inheritance of all, When a class extends another class(Only one class) then we call it as Single inheritance. The below diagram represents the single inheritance in java where Class B extends only one class Class A. Here Class B will be the Sub class and Class A will be one and only Super class.
Class A
{
public void methodA()
{
System.out.println("Base class method");
}
}
Class B extends A
{
public void methodB()
{
System.out.println("Child class method");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
B obj = new B();
obj.methodA();
obj.methodB();
}
}
Multi-level Inheritance:
In the case of multi-level inheritance, a subclass that is inheriting one parent class will also act as the base class for another class. Based on the example given below, B is the subclass that is inhering the features of parent class A and acting as the base class for C subclass. Get more additional skills from Java Online Training

public class ClassA
{
public void dispA()
{
System.out.println("disp() method of ClassA");
}
}
public class ClassB extends ClassA
{
public void dispB()
{
System.out.println("disp() method of ClassB");
}
}
public class ClassC extends ClassB
{
public void dispC()
{
System.out.println("disp() method of ClassC");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
ClassC c = new ClassC();
c.dispA();
c.dispB();
c.dispC();
}
}
Multiple Inheritance in Java
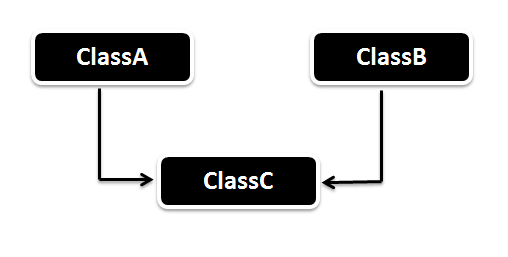
Multiple Inheritance is nothing but one class extending more than one class. Multiple Inheritance is basically not supported by many Object Oriented Programming languages such as Java, Small Talk, C# etc.. (C++ Supports Multiple Inheritance). As the Child class has to manage the dependency of more than one Parent class. But you can achieve multiple inheritance in Java using Interfaces.
Hierarchical Inheritance in Java
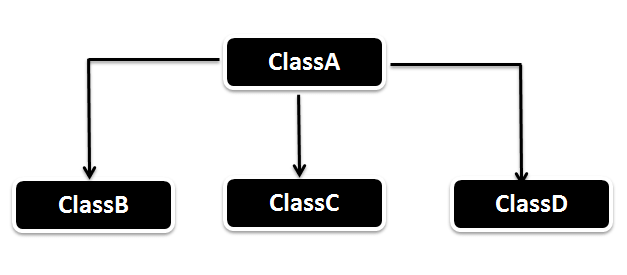
In Hierarchical inheritance, one parent class will be inherited by many sub classes. As per the below example, ClassA will be inherited by ClassB, ClassCandClass-D. ClassA will be acting as a parent class for ClassB, ClassC,andClass-D.
public class ClassA
{
public void dispA()
{
System.out.println("disp() method of ClassA");
}
}
public class ClassB extends ClassA
{
public void dispB()
{
System.out.println("disp() method of ClassB");
}
}
public class ClassC extends ClassA
{
public void dispC()
{
System.out.println("disp() method of ClassC");
}
}
public class ClassD extends ClassA
{
public void dispD()
{
System.out.println("disp() method of ClassD");
}
}
public class HierarchicalInheritanceTest
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
ClassB b = new ClassB();
b.dispB();
b.dispA();
ClassC c = new ClassC();
c.dispC();
c.dispA();
ClassD d = new ClassD();
d.dispD();
d.dispA();
}
}
To get in-depth knowledge, enroll for live free demo on Java Certification Course
Hybrid Inheritance

This is mix or two or more types of inheritance discussed earlier. Like the multiple inheritances, hybrid inheritance is also not supported in Java through classes but you could make it possible again through interfaces.