The IT sector today aims to achieve optimal efficiency. However, this is not an easy task as they face many roadblocks on the way. Legacy systems are still in use, which can slow them down considerably. In this what is ServiceNow blog, I’ll be going into how ServiceNow came into existence in the ITSM sector, as well as how it’s grown to become a full-fledged enterprise cloud solution.
Why ServiceNow?
ServiceNow had its roots set in ITSM since 2012. However, with changing technology and the advent of cloud, it created its niche as a cross-departmental platform which functions as an enterprise cloud solution which is built on top of all other applications. Its ability to create workflows which automate the process of data extraction makes it a unique offering in today’s cloud space.
ServiceNow has a raving customer base which returns to its platform each year. Let’s now look at the different cloud deployment models and where ServiceNow fits in.
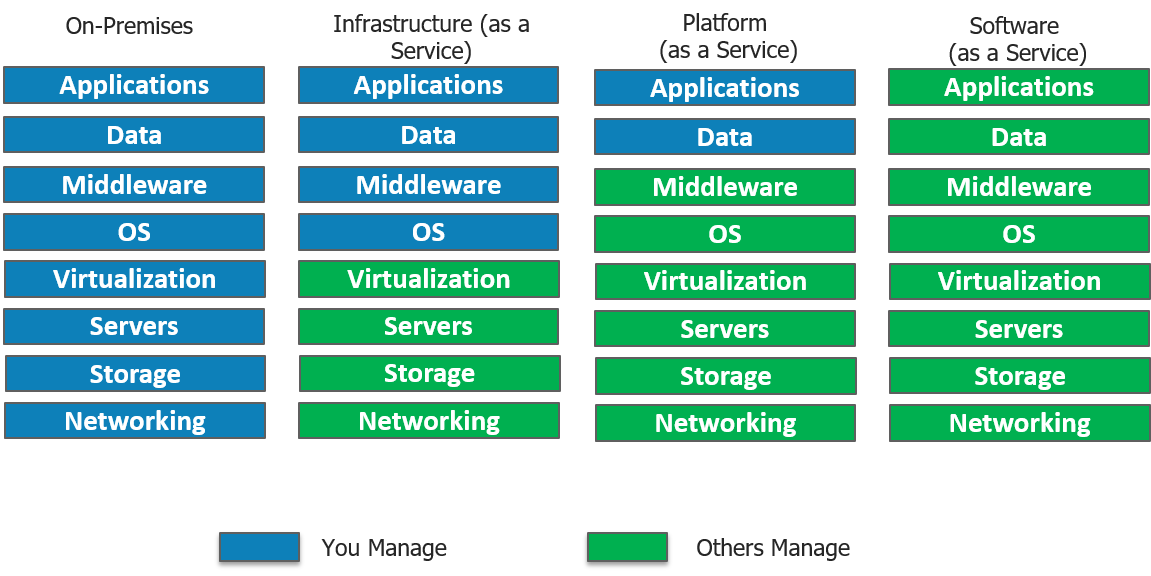
IaaS(Infrastructure as a service)
- In short, IaaS gives you a server in the cloud(virtual machine) that you have complete control over.
- In Iaas, you are responsible for managing everything from the Operating System on up to the application you are running. For more info Servicenow Training
PaaS(Platform as a Service)
- With PaaS, you have a combination of flexibility and simplicity.
- Flexible because it can be tailored to the application’s needs.
- Simple as no need of OS maintenance, versions, patches.
SaaS(Software as a Service)
- A software distribution model in which a third-party provider hosts applications.
- Instead of installing and maintaining software, you simply access it via the Internet.
- Automatic updates reduce the burden on in-house IT staff.
Where does ServiceNow fit in?
ServiceNow which started off on a SaaS model catering to ITSM, has also ventured into PaaS cloud model, in which the entire organization’s business processes can be managed by a single system of record. ServiceNow provides the infrastructure needed to perform data collection, storage, as well as application development all on a single platform. Although ServiceNow does not provide an in-house Iaas deployment model it does support integration to Microsoft Azure which is an IaaS model.
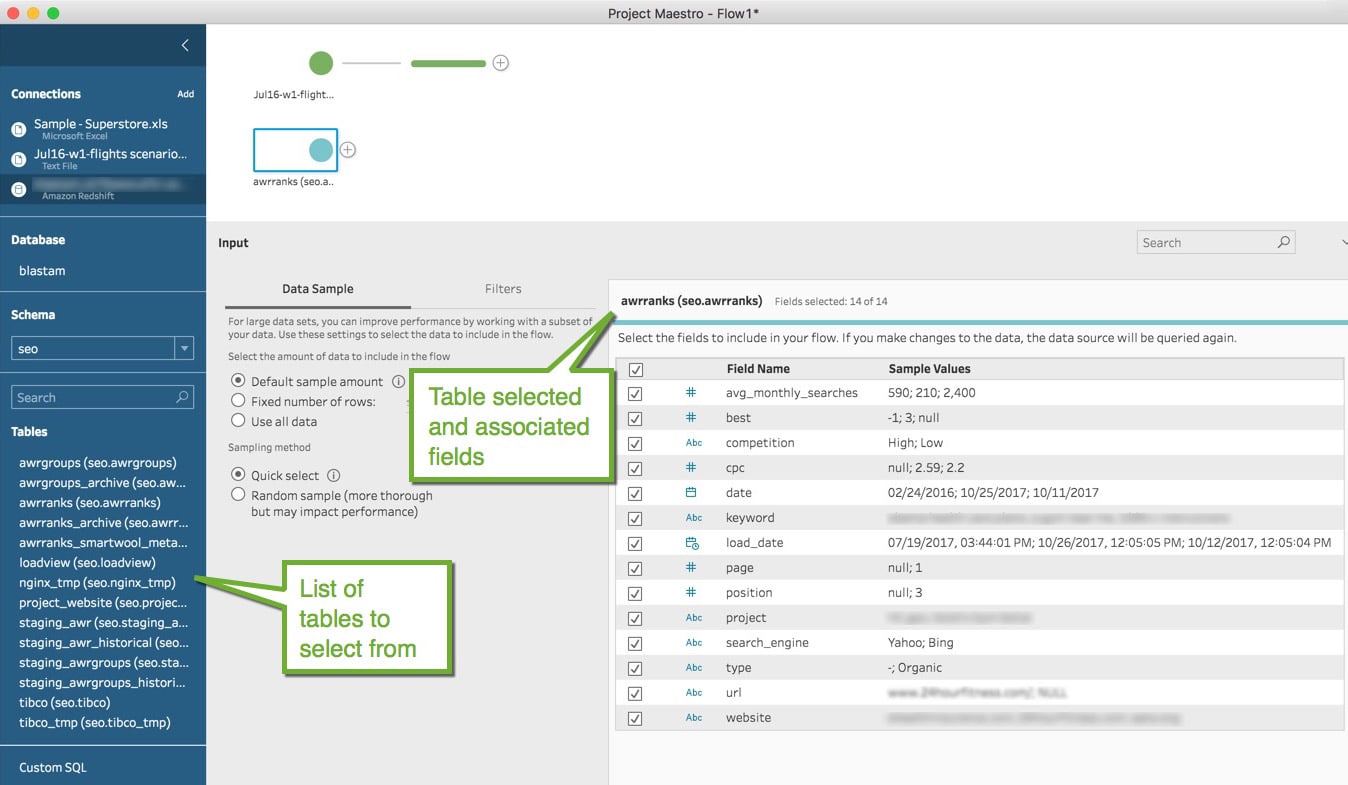
It offers configuration management database (CMDB) along with service mapping which powers service-aware applications. Service mapping shows the dependencies amongst the organization’s assets. This leads to much-needed visibility into the business environment.
Great, now let us try to address the most essential question of this blog, what is ServiceNow?
What Is ServiceNow?
ServiceNow was founded in 2004 and stepped foot in the ITSM (Information Technology Service Management) field and provided competition to established players like IBM and HP. Today it is not just limited to ITSM, even though it still forms a major part of its revenue. Now, it is has diversified into 5 major services which include IT, Security, HR Service Delivery, Customer Service and Business Applications. ServiceNow is an integrated cloud solution which combines all these services in a single system of record.
ServiceNow’s Vice President Dominic Phillips, in one of his keynotes, pointed out that while we are witnessing so much “disruption” in the consumer sector, there is a lack of efficiency in internal business workflows inside organizations.
In today’s digital era, the ease of access that Uber and Airbnb provide while booking a cab or reserving a table is the kind of experience ServiceNow wants to provide to its customers within the enterprise.
Let us now move forward to understand how ServiceNow works by looking at its architecture. Get more skills from Servicenow Developer Training
ServiceNow Architecture
The majority of cloud service offerings today, run on the age-old Multi-tenant architecture like AWS, Azure, Salesforce, Oracle, etc. The Multi-tenant architecture creates a single instance which serves multiple customers. This usually deals with complex databases which demand frequent maintenance, often leading to unavailability of resources to customers. This is why ServiceNow has adopted a Multi-instance architecture.
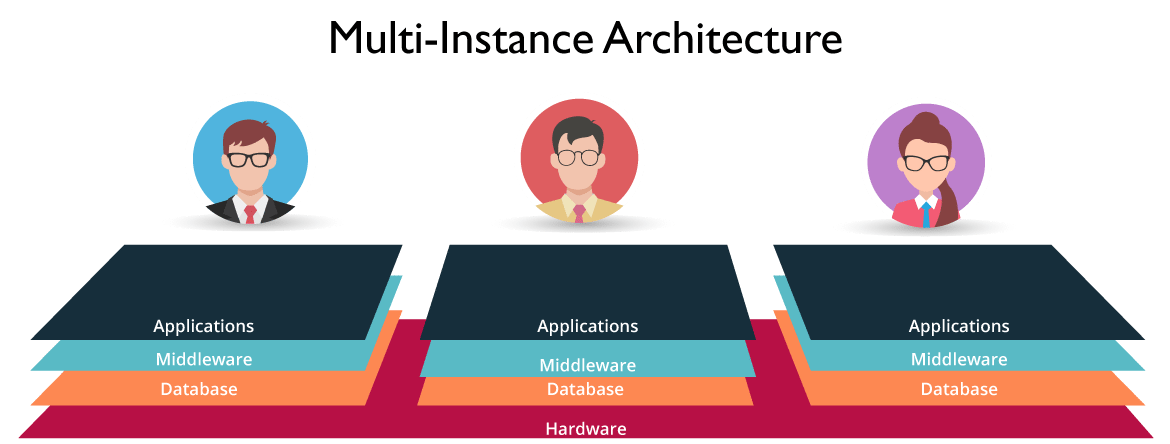
Multi-instance architecture: A unique instance is created for each employee which maintains a separate resource stack. This gives us the freedom to deal with each user’s specific needs, enabling us to deal on a customer-customer basis. E.g. customer upgrades can be deployed with respect to compliance requirements as well as the enterprise’s current needs.
In our diagram shown below, 3 customers have unique instances each with an isolated pool of resources. What this means is, while the hardware is shared, the software: Application, Middleware and Database are all separately maintained. Data Isolation is a huge advantage. This is why the performance of one customer is not influenced by another customers instance. Neat, isn’t it?
Figure: What Is ServiceNow – Multi-Instance Architecture
ServiceNow Applications
In this what is ServiceNow blog, let’s get an overview of the ServiceNow Applications.
IT Service Desk
A report found that 15 hrs out of 45 hrs in a work week are spent doing non-work related tasks. It was identified that this is due to the outdated ITSM software in use.
In ServiceNow, employees are provided with a self-service portal where they can avail IT Services by messaging the concerned department staff. ServiceNow was able to bring the ease of use of social media apps to the ITSM sector which was still lagging behind with legacy systems.
With ConnectChat, the staff can reply in real time. This can be seen as an improvement over the traditional mailing system where messages had to be sent back and forth. This supports the sharing of files across departments. An employee can attach incident files as part of the conversation enabling technicians who can then directly look up the incident records and service the request. If a user is unsure which technician is on duty he can create a group with all technicians as members. Visual taskboards allow you to assign tasks to different departments with just a drag and drop gesture.
Resolving Security Threats
In spite of having a sophisticated security management mechanism in place for threat detection, when there is a security breach, most companies face an uphill task of resolving the problem.
ServiceNow uses structured workflows which helps prioritize risks based on their severity and their impact on the organization.
Threat research would normally take up to 45 minutes using spreadsheets and manual processing.
However, automated tools provide this information inside the platform which reduces the time involved to under 20 seconds.
HR Service Delivery
Ever wondered how HR spends most of its time doing repetitive tasks like employee onboarding when they should actually be focusing on strategic tasks instead?
ServiceNow wants to do away with all that manual processing. These tasks span across different departments like IT, Facilities, Legal and Finance. ServiceNow’s single platform can be used to connect HR workflows with all these departments. Decision making is made easy with its tracking and trending tools. HR is now powered with consumer-like customizable forms to deliver satisfactory service to employees.
Customer Service
The need of the hour is to provide uninterrupted quality service yet keeping the cost constraint in mind. ServiceNow is transforming Customer Service into a Team Sport. Unlike CRM(Customer Relationship Management) which is limited to customer engagement, ServiceNow Customer Service Management (CSM) operates by Connecting the right people, systems and workflows.
Customer Service is not limited to just resolving customer tickets. Whenever a customer is facing an issue, we need to find its root cause. This will reduce case(tickets) volume in the long run. ServiceNow comes with Service Mapping which provides cross-functional information to discover the initial point where the error was first noticed.
ServiceNow makes it easy to dispatch across different departments like engineering, field services, legal, etc. Take the example of the coffee maker that’s not working. The field agent is notified of its possible problem even before he starts his conversation with the customer. The customer is notified proactively with real-time notifications ensuring customer satisfaction and resolving issues at lightspeed.
Business Applications
ServiceNow comes with a drag and drop approach which allows you to customize Business Apps without writing a single line of code. For the experienced developer, you will never have to start from scratch again as you can choose from reusable components, workflows and link barriers across departments using information from the cloud.
Let’s now move ahead in this what is ServiceNow blog and understand what is a PDI.
Personal Developer Instances (PDI)
PDIs are meant for a walkthrough of the ServiceNow features. It can be used by developers, customers or even partners. The motive behind this instance is, it does not interfere with the production instance. Application ideas can be tested on PDI’s however, it will not be added to the final application repository.
Instances may be kept as long as there is regular activity. To be considered as active you need to either create applications or write scripts within 14 days. Now that we are aware of PDI’s, let’s move ahead and explore the ServiceNow Platform.
Creating A Personal Developer Instance(PDI)
To request a personal developer instance, the ServiceNow developer program provides you with a fully-functional instance, sized for single developer use. Let’s explore the two options to request a personal developer instance.
Step1: Log into the developer site at https://developer.servicenow.com.
Step2: Request a PDI by doing any of the following actions.
- From the dashboard homepage, click Request Instance.
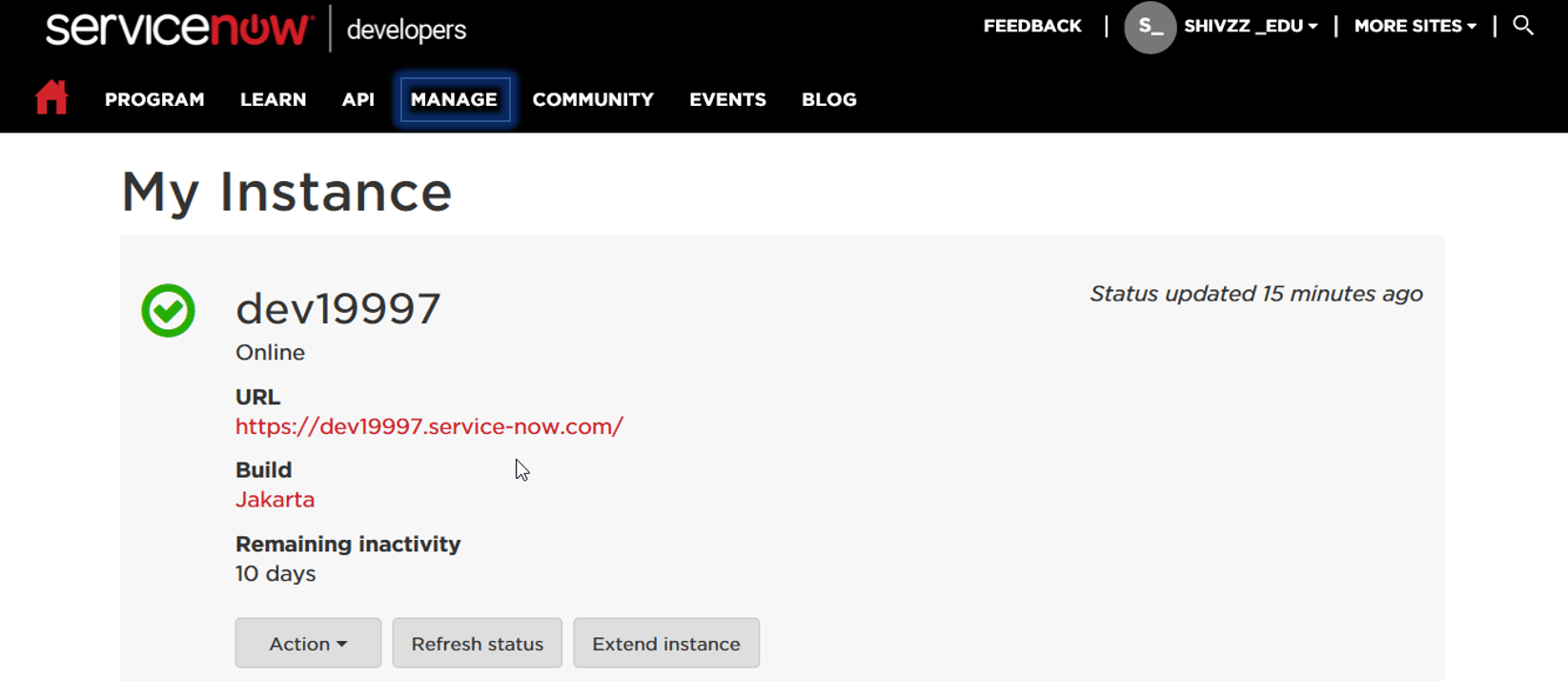
From any page on the developer site, navigate to Manage >> Instance and click Request Instance.
On successful registration, you will get an instance copy as shown above. You can click on the URL and login with your credentials.
To get in-depth knowledge, enroll for a live free demo on Servicenow Online Training























.png?width=1634&name=image%20(8).png)

.png?width=1142&name=image%20(9).png)





