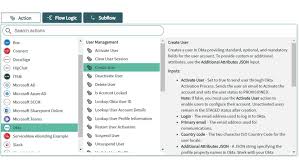
Integrating cloud platforms with traditional ERP platforms like SAP is difficult, and ERP integration methods like SAP’s Application Link Enabling (ALE) are limited and inflexible. Attempts to improve flexibility have compounded the complexity. For most IT organizations, integrations between systems is a difficult, budget-consuming endeavor. Since large ERP vendors are systems of record, their requirements control the relationships.
Workday® is breaking the logjams by creating packaged integration solutions, flexible tools, and advanced developer platforms.
As more SAP users implement Workday® as the system of record for worker information, Workday® has standardized the approaches to SAP integration, among others in its cloud integration platform. For more info Workday Training
Workday® Integration Services
Workday® has unified all the many ways to integrate data flow into a single Enterprise Service Bus (ESB). The platform provides three ways to deploy integrations: packaged services, tools for business users, and tools for integration developers.
Connectors and Toolkits. Where the number of integrations makes it feasible, Workday® creates and maintains packaged services pre-configured for specific external platforms or toolkits for external vendor types. These include payroll vendors, benefits providers, financial systems, procurement, and many others.
Enterprise Interface Builder is a graphical tool for business users and analysts. Users can extract and load data using Excel spreadsheets, and package data sets using standard data formats, protocols, and transports.
Workday® Studio is a full-featured developer tool for creating and maintaining Web Services integrations. It includes a graphical IDE and pre-packaged components. It is customizable with Java, Spring, or third-party interfaces. For more details Workday Course
Workday® Services
Workday® maintains internal services that make data integration easier and more transparent than traditional ETL operations. These are configurable services that handle data extractions without programming.
Business Management Services return data sets from the major functional areas in Workday®. The operations correspond to business events and business objects in Workday®. They return large data sets but can be configured to return subsets.
Reporting Services, known as Reports as a Service (RaaS), are used to define and create custom REST/SOAP APIs. You define the data set and package it for Workday® or any third-party integration tool.
Outbound Messaging Services provide real-time notifications to external applications when business events occur in Workday®. The workflow behind the event is configured to push an outbound message to a subscribing ALE system. The subscribing system can then query Workday® to get details about the event.
Infrastructure Services expose Workday® metadata to external applications to extend the functionality of integrations. External applications can monitor the execution of integration events to see the status and when and how data will come from Workday®.
SAP/Workday® Integration
Integrations between Workday® and SAP use a combination of Workday® Services, Connectors, and Studio Web Services APIs.
The most common implementation model for SAP customers who use Workday® is to make Workday® the system of record for people information and SAP the financial system of record. Learn more additional skills from Workday Online Course
Maintaining SAP HCM
SAP maintains Human Capital Management information in Organization Management (OM) and Personnel Administration (PA). Once data migrates to Workday® Human Capital Management, OM and PA must still be maintained for payroll processing, financials, and workflow.
Organization, Position, and Job Connectors or Web Services in Workday® update OM in SAP. The Worker Connector or Web Service updates PA. The Workday® Document Transfer and Deliver process transforms the data into the SAP IDoc XML format.
Since the Workday® cloud is XML with an XSD, standard XSLT will transform the data into the data format the SAP IT group specifies. Workday® provides an XSLT library for validations and error-handling.
Cost Center Updates
When cost center information changes in SAP, it is necessary to update Workday® when the event happens. The event triggers an IDoc to a Workday® Organization Connector or Web Service.
Worker Updates
Depending on the data needs of the existing SAP modules, updates to Worker records in Workday® will need to initiate a simple Worker Connector/Web Service or a Worker Full Stack via Web Services to SAP Personnel Administration.
SAP Mini Master
SAP created a small file requirement for maintaining Personnel Administration information for workflow routing in SAP applications. The typical file will have about a dozen fields.
For Mini Master files, the best practice is to use Connectors to generate the data.
- Integration maps are configurable, reducing the risk of failure by eliminating extra processing nodes and the need for programmatic troubleshooting.
- Workday® Core Connectors detect data changes on an object or event and deliver only those changes in the final file extract. The integration can be configured to manage the types of changes detected in the transaction log. SAP infotypes can be mapped to Workday® transaction types.
SAP Payroll
If Mini Master is the current method of feeding master data to Payroll, the data feed will need to be expanded to run payroll, depending on what countries payroll may be running. This method may not capture sufficient information where in the cases of proration, retroactivity, and adjustments.
Workday® Cloud Connect for Third-Party Payroll can be a solution. It takes a top-of-stack approach by taking a snapshot of the transaction history and sending a full or changes-only extract file to SAP.
Workday® Studio will be the option if transactions must be sequenced.
Cloud Connector Workday® Studio will also be the best options for using a payroll processor other than SAP.
Using Workday® Payroll
If you are using Workday® Payroll, you will need to update SAP Financials after each pay run. In that case, a Workday® Custom Report and Enterprise Interface Builder will handle the job without programming.
To get in-depth knowledge, enroll fora live free demo on Workday Online Training